India Teams Up with NASA for Groundbreaking NISAR Satellite Launch
India has launched the NISAR satellite, developed in collaboration with NASA, to monitor climate change and natural disasters. The satellite features dual radar frequencies for precise Earth imaging and will provide valuable data for scientists globally. The mission strengthens India's space cooperation with the U.S. and its global scientific standing.
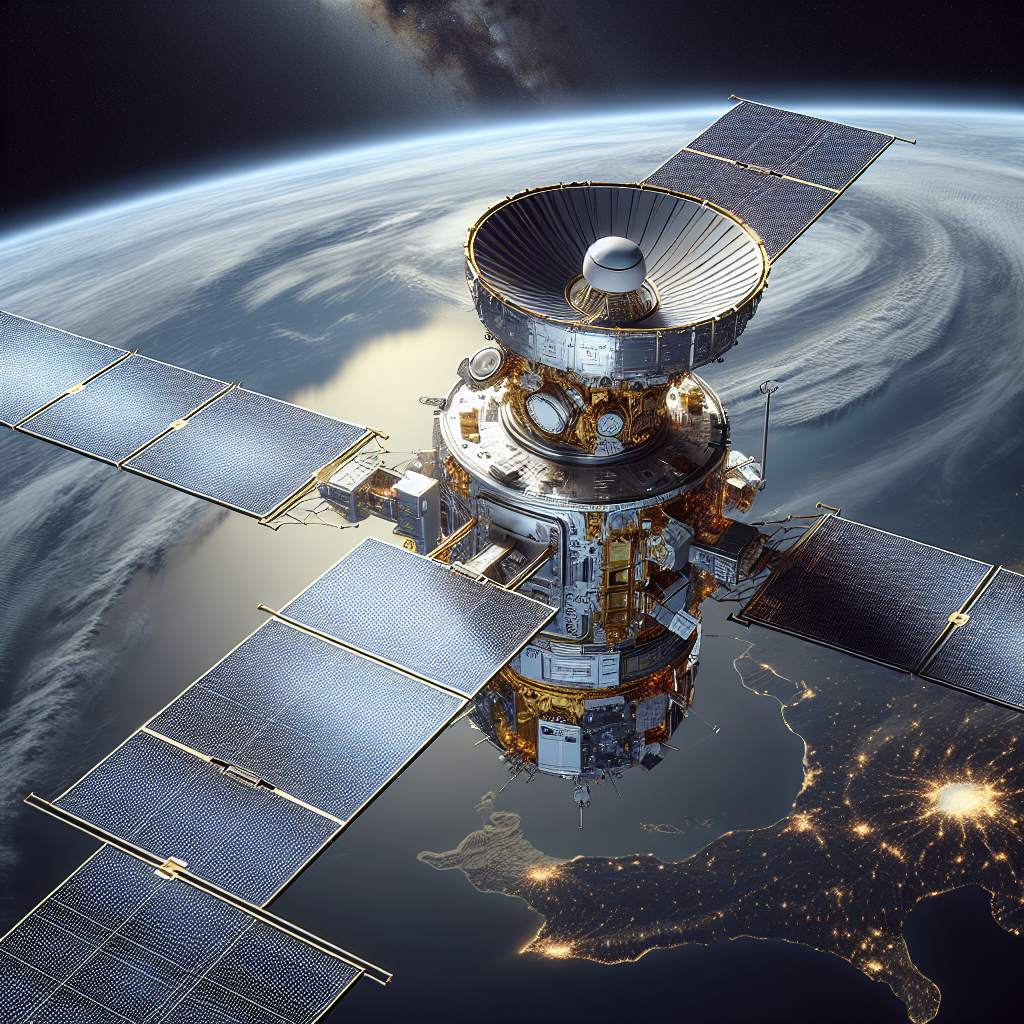
On Wednesday, India launched a groundbreaking $1.5 billion radar imaging satellite developed in collaboration with NASA. Named the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR), this satellite aims to enhance global monitoring of climate change and natural disasters. As a pioneering collaboration between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and NASA, NISAR marks a significant milestone.
The satellite was launched from India's Satish Dhawan Space Centre, highlighting India's growing prominence in space missions. NISAR is the first radar imaging satellite to employ two radar frequencies—NASA's L-band and ISRO's S-band—enabling it to detect minute Earth surface changes. It resides in a near-polar Sun-synchronous orbit, 747 kilometers above Earth, and will map the planet every 12 days.
The data generated will be accessible globally to facilitate scientific research and disaster response. With a service life of at least five years, NISAR's mission is a testament to India's ambition in the space sector, aligning with global initiatives like Chandrayaan-3 and Gaganyaan. India's space endeavors now include plans to establish a space station by 2035 and further international cooperation.
(With inputs from agencies.)










